CBT
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is the most common form of therapy available for people experiencing health anxiety.
Individual non-facilitated self-help based on the treatment principles of CBT, and CBT are the recommended treatments by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Clinical Evidence (NICE) for people with generalised anxiety disorders, though there are no specific NICE guidelines for health anxiety at the present time.
Evidence suggests that psychological treatments for health anxiety can improve quality of life (Thompson and Page, 2007).

CBT is a therapy that focuses on our cognition, (the way we think) and our behaviours (the way we act). The main concept behind CBT is that our thoughts about a situation affect how we feel and how we behave. We tend to assign meaning to specific situations. Often it’s not the actual situation causing our anxiety, but the meaning accurate or not. When you have anxiety, your thoughts tend to be given a lot of meaning, and thus, a lot of power. The diagram below demonstrates how these elements interlink.
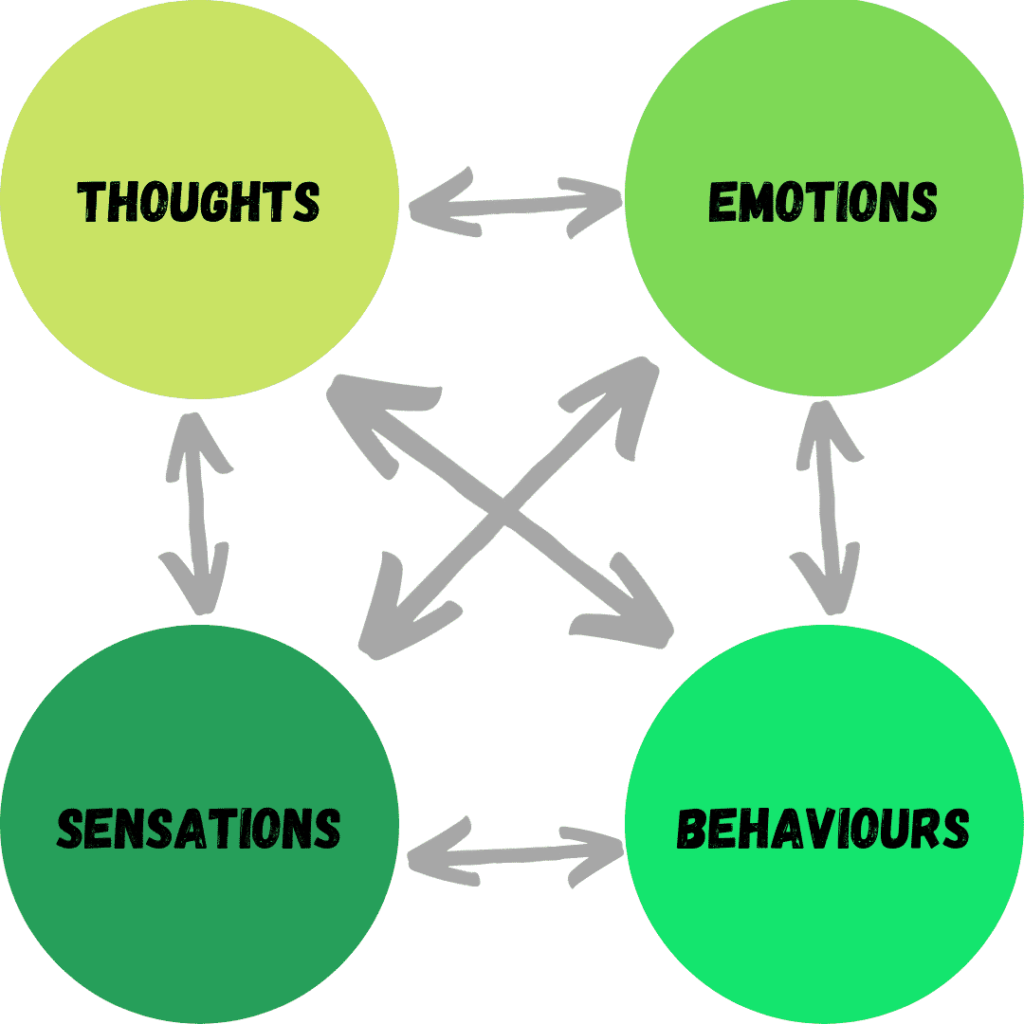
CBT can enable you to become more aware of your thoughts and behaviours, and how they interact. It is possible to learn to approach anxious situations differently and learn to tolerate discomfort and uncertainty to a greater degree.